What Is APR and How Does It Work?
The annual percentage rate or APR indicates the true cost of borrowing money. It is a determinant in credit cards or other forms of credit applications. Hence, it’s crucial to consider the APR before entering any financial agreement. There are many ways in which APR is related to credit scores, one being that if you have a good credit score, there is a possibility that your APR will be lower. This leads to lower costs in borrowing. This article will discuss what an APR rate is, types of APR, means of APR calculation, and how your scores affect it.
See Better Credit Now — Discover what AI-powered credit repair can do for you!
Try NowWhat Is APR (Annual Percentage Rate)?
The APR is the yearly interest rate + other associated fees you incur when acquiring any loan. It typically includes:
- Interest Rate
- Loan Origination Fees
- Mortgage Fees
- Closing Costs
- Any Other Fees Charged by Lenders
Hence, it is deemed a more realistic indicator of the true cost of borrowing money.
Why APR Is Important in Credit Applications?
- Cost Comparison: Borrowers use APR to compare the total costs of credit options.
- Financial Planning: Helps determine the affordability of loans or credit products.
- Risk Assessment: A high APR may deter borrowers or indicate higher risk for lenders.
When Is APR Used?
APR is used to calculate the cost of borrowing in the following instances:
- Credit Cards
- Mortgage
- Personal Loan
- Auto Loan
- Business Loans
- Home Equity Loan
- Medical Financing
- BNPL Plans
- Mortgage Refinancing
Depending on the scenario, APR can be used to calculate the total cost of borrowing or determine the interest rate on outstanding balances on the debt when payments are not made by the due date.
Types of APR
| Type of APR | Definition | Applicable |
| Fixed Rate | As the name suggests, it’s a fixed (benchmark) rate that does not fluctuate depending on the U.S. prime rate, regulations, etc. throughout the loan duration. However, the rate can change when there are any default payments. | ▪ Mortgage ▪ Auto Loan ▪ Personal Loan |
| Variable APR | When the rate increases or decreases with the U.S. prime rate or regulations. | ▪ Credit Card ▪ Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMs) |
| Introductory APR | It’s a temporarily low or 0% APR, which is valid for a limited time for promotional purposes. Hence, it’s also called promotional APR. | ▪ Credit Card ▪ BNPL Services ▪ Medical Credit Cards |
| Purchase APR | It’s the interest charged on any purchases that you make using your credit card. | ▪ Credit Card Purchases |
| Balance Transfer APR | It’s a charge on the balance, i.e., credit card debt that you transfer from one credit card to another. | ▪ Balance Transfer Credit Card |
| Cash Advance APR | It’s the interest applied to cash withdrawals made using a credit card. The interest is usually much higher than on regular purchases. | ▪ Credit Card Cash Advances |
| Penalty APR | It’s charged when you miss a payment and have to pay a penalty APR, which is much higher than the original APR. | ▪ Loans ▪ Credit Card ▪ Payday Loan |
| Deferred Interest APR | When interest is deferred for a specified promotional period but applied retroactively in case of default or after the deferred period. | ▪ Promotional Financing ▪ BNPL Services |
| Subprime APR | It’s a higher-than-average interest rate that is charged to those with lower/poor credit scores. | ▪ Auto Loans ▪ Credit Card ▪ Loans from third-party providers |
How Is APR Calculated?
Let’s break it down with an example:
Say, loan amount: $10,000
Interest Rate: 15%
Interest Amount: $1,500
Other Fees Paid: $350
Loan Term: 390 days
| Steps | Description | Calculation |
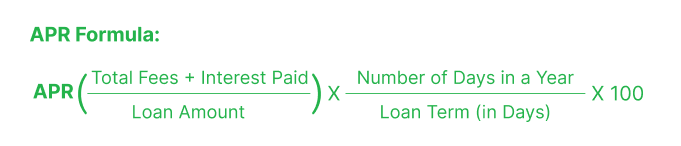
| Step 1 | Add the total interest paid and fees, then divide by the loan amount. | ($1,500 + $350) ÷ $10,000 = 0.185 |
| Step 2 | Multiply the resulting cost by the number of days in a year (i.e., 365), divided by the loan term in days. | Annualized Cost = 0.185 × 365/390 = 0.1731 |
| Step 3 | Multiply the result by 100 to calculate the annual percentage rate. | APR= 0.1731 × 100 = 17.31% |
How to Calculate Monthly APR?
For this, first, you need to calculate the daily periodic rate. Follow the below steps:
| Steps | Description | Calculation |
| Step 1 | Divide the annual percentage rate (APR) by the number of days in a year (365) to calculate the daily periodic rate. | Daily Periodic Rate = 17.31% ÷ 365 = 0.000474 |
| Step 2 | Multiply the daily periodic rate by the number of days in a month (30) to calculate the monthly periodic rate. | Monthly Periodic Rate = 0.000474 × 30 = 0.01422 |
| Step 3 | Multiply the resulting figure by the average daily balance to calculate the monthly APR cost. | Monthly APR Cost = 0.01422×10,000=142.20 |

What Factors Impact APR?
| Factors | Description | Examples |
| Type of Loan | Some loans have naturally high APRS while others have low APRs based on the nature of the loan and associated risks. | Unsecured loans usually charge a higher APR, i.e., Payday Loans Most secured loans (i.e., backed by collateral) may have lower APR. |
| Lender | Each lender may have varied policies and risk-taking abilities that impact APR. | For instance, a financial institution like a bank may offer a personal loan at a lower APR than a private lender, which may charge more interest for the same loan amount and term. |
| Credit Profile | Borrowers with higher credit scores are often offered lower APRs due to reduced risk for lenders. | Someone with an excellent credit score may get favorable terms and lower interest rates. However, if your scores are poor, the interest can be relatively higher. |
| Associated Fees | Fees such as origination, closing, and administrative charges can increase the APR. | High origination fees or closing costs on a mortgage/loan can increase the APR above the stated interest rate. |
| Regulations | Each state usually have different regulations regarding specific loans and interest rates limiting what lenders can charge. | Some states set a cap on payday loan APRs. |
Why Is APR Important?
Knowing the APR before obtaining any new credit gives you an idea of how much you will ultimately pay for the loan in the long run. The APR is important, as it makes comparing different lenders and loan options easier.
What Is a Good APR?
It differs based on various factors and the credit score range of the applicant. For instance, for a credit card at a current standard APR of 24.26%, the following can be considered good APR:
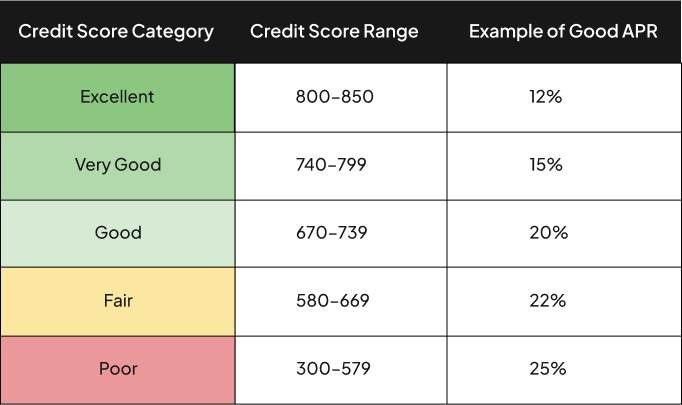
However, these rates are approximate and subject to lender policies. There is no general benchmark so APR can vary based on type of loan, purpose, issuer policies, market conditions, and many other factors.
APR vs. Interest Rate: What’s the Difference?
Interest Rate Meaning: Whenever you borrow money, you have to pay an additional charge on top of the original sum, which is the interest amount. The percentage of the interest being charged is the interest rate.
APR Meaning: This is the annual interest rate plus other charges. Typically includes origination fees, closing costs, and any other associated fees that lenders may charge.
| Criteria | Interest Rate | APR |
| Calculation | Based solely on the principal amount. | Takes into account both the interest rate and other loan-related costs, spread out over the loan term. |
| Costs Included | Covers only the interest. Does not include lender fees and additional costs. | Includes fees such as origination fees, processing fees, and closing costs in addition to the interest. |
| Importance for Borrowers | Useful for understanding the base cost of borrowing without any additional fees. | More relevant for comparing loans from different lenders. |
| Example | A loan with a 4% interest rate has a fixed charge on the borrowed amount. | A loan with a 4% interest rate and 1% origination fee and closing costs might have an APR of 4.5%. |
What’s the Impact of a High vs. Low APR?
The high and low APR can impact your finances in different ways, such as:
| High APR | Low APR |
| People with low credit scores usually have to pay high APRs | People with high credit scores usually have lower APRs |
| High Monthly Payments | Low Monthly Payments |
| High overall cost of borrowing | Lower overall cost of borrowing |
| May strain the budget | More affordable and less impact on finances |
| Can be challenging to pay off quickly | Faster repayment is feasible |
| Reduces borrowing power | Relatively easy to get a new line of credit in the future. |
| Can be difficult to manage timely payments, and missing a payment can severely impact the credit scores. | Manageable payments make it easy to repay on time. |
| Examples: Payday loans, credit cards | Examples: Mortgage, loans from bank |
How to Lower the APR for a Credit Card?
To enjoy a lower APR on a credit card, here’s what you can do:
- Maintain a Good Credit Score
The best way to ensure the APR on borrowing is minimal is by maintaining an excellent credit profile. If your scores are in the excellent range, you can get the best deals on new lines of credit including lower interest rates. For this, you can use a DIY credit repair/builder app.
- Balance Transfer to Another Credit Card
A balance transfer offer allows an individual to move the balance from a high-interest credit card to a new card, carrying low or sometimes even 0% promotional APR for a given period. So, if you find a special offer balance transfer card, with 0% APR for 6 months or longer it may be worth considering.
Pro Tip: Pay off the balance in full before that promotional period runs out to avoid APR on this balance.
- Negotiate with Lender
If you have a good credit standing and pay your bills on time, you may be able to negotiate with the lender for a lower APR. However, for this, it's crucial to improve your credit habits and work on building a favorable credit profile.
Repair Your Credit with AI — Tap into AI Now!
Get StartedHow to Build Your Credit to Reduce APR?
There are many ways to strengthen your credit for more favorable terms and APR, such as:
- Pay Your Bills Timely
Missing even one payment can set you back 100 points. Hence, it's crucial to financially plan ahead and make timely payments and don’t have any defaults on your profile.
- Analyze Your Credit Report and Dispute Inaccuracies
Also, fetch a copy of your credit report and check for any potential errors or inaccuracies that may be negatively impacting your credit. If there are any mistakes you can raise a dispute with the relevant credit bureau to get it fixed. This can help improve your credit rating. To make it easy, you can download the CoolCredit app. It will analyze your credit score and offer actionable tips for working toward better credit.
- Regularly Monitor Your Credit Report
While diligently working on your credit you also need to regularly monitor your credit report to stay on track. An AI-assisted app like CoolCredit can come in handy. This can help you analyze your credit report using AI to highlight any negative items as well as give you tips on how to improve your credit score step by step.
- Keep a Reasonable Gap Between New Credit Accounts
Avoid opening multiple accounts within a short span as this means back-to-back credit inquiries, which result in low credit scores. As a standard rule keep a minimum of 6 months gap between each credit account.
- Minimize Credit Utilization Rate
Keeping your credit balance well below the maximum credit limit and consistently good payment habits can significantly help strengthen your credit profile.
Conclusion
Familiarizing yourself with APR rates and other associated factors can be beneficial in helping compare lenders and loan types when you are thinking about borrowing, especially if you need long-term credit. You can usually avoid paying a high APR by working on improving your credit scores and maintaining a great payment history. However, it requires continuous efforts.
The CoolCredit app can prove to be your ally. Learn all about CoolCredit and its credit repair features today!
FAQs
Q: What Is APR Rate?
A: It’s the total cost of borrowing, including the interest rate and additional fees such as closing costs, lender fees, and other associated fees.
Q: What Is a Good APR Rate?
A: An APR below the national average is usually considered good. So, an APR below 24.26, the current national rate, is a good APR. However, it may also differ based on the credit scores.
Q: What Is a High APR?
A: APR above the national average, which currently hovers at 24.26 is considered to be a high APR; therefore, an APR equal to, or above 25% is a high APR.
Q: What Is the Difference Between APR vs. APY?
A: APR is “Annual Percentage Rate” and APY is “Annual Percentage Yield," which are vastly different. In contrast to APR, APY is the rate at which you receive interest on investments, savings, or other financial products.
Q: How to Calculate the Daily APR Rate?
A: Simply divide the APR by the number of days, i.e., 365, and you’ll get the daily rate.